The rubber bearings have characteristics common to both fixed and mobile bearings. Allow rotations around any axis.
This happens because the rubber, deforming at almost constant volume, changes geometry allowing the superstructure to rotate. Vulcanized internal metal sheets are opposed to this movement.
In the moment in which, on the other hand, the rubber bearing undergoes the effect of horizontal forces it deforms minimally and in any case on the basis of the rubber compound used, the duration of the applied load or the temperature.
When the elastomeric bearing undergoes the action of a pair of two force vectors, parallel and having opposite directions, having points of application at a distance that is not zero (rotations from bending actions M), the rubber bearing reacts by keeping the surfaces of contact with the superstructure ( with the deck ) and with the substructures of the bridge/viaduct.
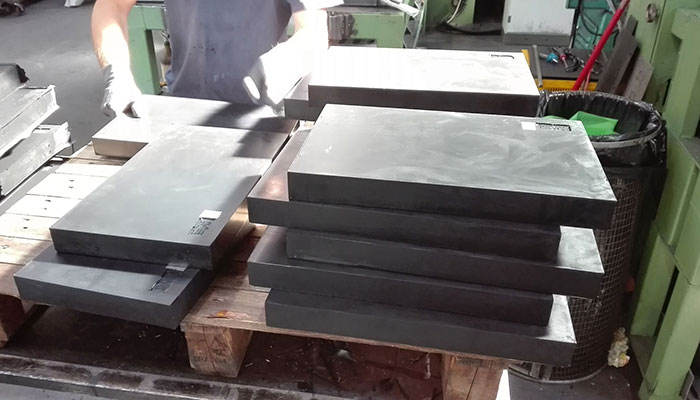
The reinforced elastomeric bearings consist of a block, usually a parallelepiped, in elastomer (natural or synthetic rubber) which has steel layers inside. The process that allows the union of these two materials, as for the expansion joints in rubber / steel, is the vulcanization. The internal steel sheets are slightly smaller than those of the rubber layers and therefore, remaining embedded in the elastomer, they are protected against external agents and corrosion.
There are rubber layers on both the upper and lower surfaces, ie there are no external plates. The transfer of horizontal loads, therefore, takes place only by friction between the rubber and the structure of the bridge/viaduct. They are characterized by modest dimensions and maximum ease of installation. They are fixed type rubber bearings.

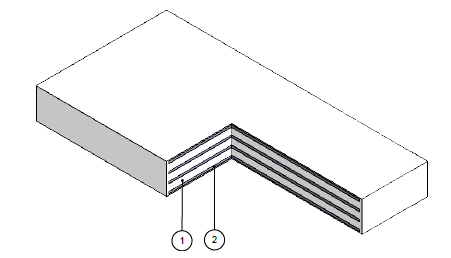
There are layers of steel on both the upper and lower surfaces ie in addition to type B, there are external vulcanised plates for connection to the sub / superstructure of the bridge or viaduct. This type of bearing, unlike that of type B, is safe against slippage as the steel plate at the base (the larger of the two) is connected to the substructure of the bridge by means of log bolts while the upper one has a pin that mates with a hole present in the counterplate, embedded in the casting in the case of beams in CA and CAP, or welded in the case of metallic superstructure. Anchoring in one direction allows easy installation and replacement. They are fixed type supports even if, by allowing deformations in any direction of the horizontal plane and generating elastic reactions of proportional intensity to the same deformations, they can be defined as "semi-mobile" reinforced rubber bearings.
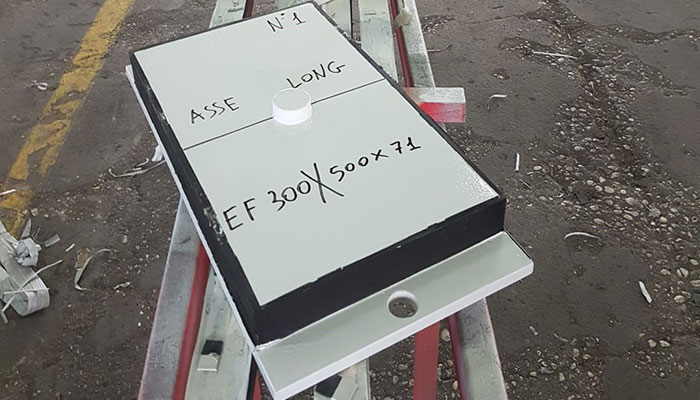
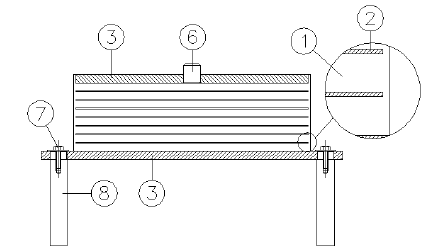
It has upper and lower vulcanised plates, such as in reinforced C-type elastomeric bearings for bridges and viaducts. The substantial difference with the latter is that, in order not to induce excessive deformations of the rubber, a PTFE sliding surface is also provided, housed in a recess obtained on the upper plate and a stainless steel plate welded to an additional external plate which has anchor bolts to the superstructure of the bridge/viaduct; these two surfaces (PTFE / INOX) are in contact with each other and having a very low friction make this elastomeric bearing of a mobile type; in fact, wide horizontal displacements are allowed (in one or both directions, transverse and longitudinal). This solution, a little less economical, is recommended when the displacement of the bridge is important. For sliding in a single direction of the viaduct or of the bridge (unidirectional elastomeric bearings) guides on the rubber bearing are used, in their absence we are in the presence of multidirectional rubber supports.

All the surfaces of the external components, to avoid corrosion, are coated with high-performance paints that are applied with painting cycles that comply with the EN 1337 part 9 standard.